Lab Diamonds vs. Natural Diamonds
At first glance, lab-grown and natural diamonds look identical. Both are pure carbon, radiating the same brilliance, fire, and durability that make diamonds so timeless. The main distinction lies in their origin.
Natural diamonds are born deep within the Earth’s mantle, formed over billions of years under immense heat and pressure. Each one is mined from the earth, carrying with it a unique story shaped by nature and time.
Lab-grown diamonds, by contrast, are created in high-tech laboratories. Using advanced methods that replicate the Earth’s natural process, these gems are grown in just a matter of weeks. Despite their different beginnings, they share the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as natural diamonds.
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds offer stunning beauty and lasting strength, making them equally perfect choices for fine jewelry and engagement rings.
The 4Cs of Diamonds

Diamond Shapes
As the name suggests, shape (round, princess, radiant, etc.) describes a diamond’s form, primarily as viewed from above. All diamond shapes have different attributes, but overall the beauty of the individual shapes is a matter of personal taste.
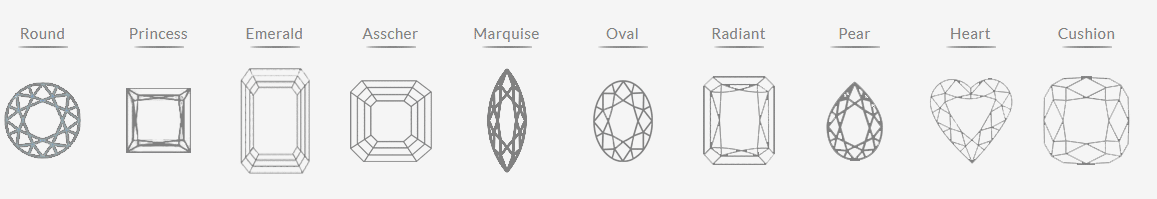
Choose Your Diamond Shape
Since all diamond cut styles are very different, unique characteristics determine quality for each shape. Select your preferred shape below and learn how to recognize the most beautiful diamond in that shape.

Round
The round brilliant cut is the most popular diamond shape used in jewelry today. Diamond cutters have been using the physics of light behavior and mathematics to optimize fire (flashes of colored light reflected back from the diamond) and brilliance (light reflected up from the surface of the diamond) in a round diamond. To get a good balance of brilliance and fire of a round brilliant diamond select one of the two highest cut grades (Excellent or Very Good).


Princess
This is the most popular non-round diamond. Its unique cut makes it popular in engagement rings. The princess cut has pointed corners and is traditionally square in shape. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in its corners.


Emerald
The pavilion (bottom portion of the diamond) makes this shape different. It is cut with rectangular facets. It has a larger open table and hereby highlights the clarity of the diamond. To optimize appearance it is advisable to choose an emerald cut with a higher clarity grade (above SI). If you prefer an emerald cut with a squared outline, look at the Asscher cut diamond.


Asscher
This shape is very similar to the emerald cut, except that it is square. The Asscher cut also has a pavilion (bottom portion of the diamond) that is cut with rectangular facets in the same way as the emerald cut. To optimize appearance it is advisable to choose an emerald cut with a higher clarity grade such as VS. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in its corners.

Marquise
The shape of a marquise diamond allows cutters to maximize carat weight, giving a much larger-looking diamond. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the points of the marquise. This style of cut looks beautiful set with round or pear-shaped side stones and the length of the marquise makes fingers appear long and slender.


Oval
Oval diamonds have brilliance similar to a round diamond. They are very popular as their length can accentuate long, slender fingers.


Radiant
Trimmed corners are the unique feature of this style of cut. They help make the radiant cut versatile for use in jewelry. Radiant cuts look most stunning when set with either baguette or round side diamonds. Radiant cuts vary in their degree of rectangularity.


Pear
This style of cut is also called a teardrop because of its single point and rounded end. The look of the pear shape makes it very popular in diamond jewelry. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the point of the pear. If you choose an elongated pear shape, the length of the diamond can create a slimming illusion on the fingers.


Heart
The heart is a symbol of love and this makes it a popular choice for use in jewelry. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the point of the heart and corners.


Cushion
Cushion cut diamonds are also known as pillow cut diamonds, they have rounded corners and larger facets. The larger facets highlight the diamond’s clarity and therefore to optimize appearance it is advisable to choose a cushion cut with a higher clarity grade (above SI).

GIA Diamond CertiFication
GIA Diamond Grading Standards
GIA diamonds are examined by a minimum of four highly trained diamond graders and gemologists. At each step of a diamond’s evaluation, a more senior staff member independently grades the stone. To ensure impartial evaluations, the distribution of diamonds to graders is a completely random process.
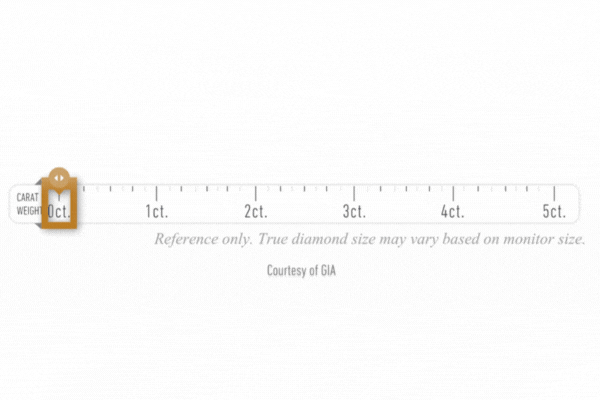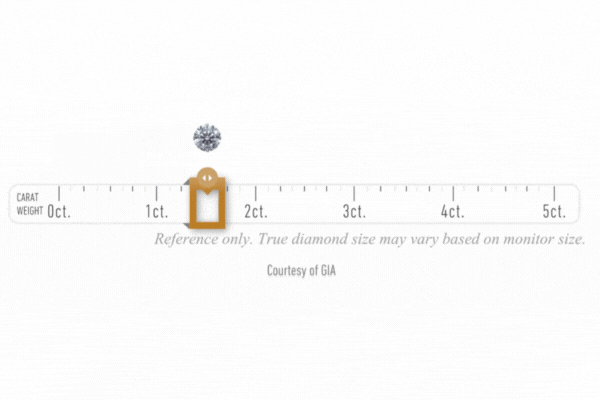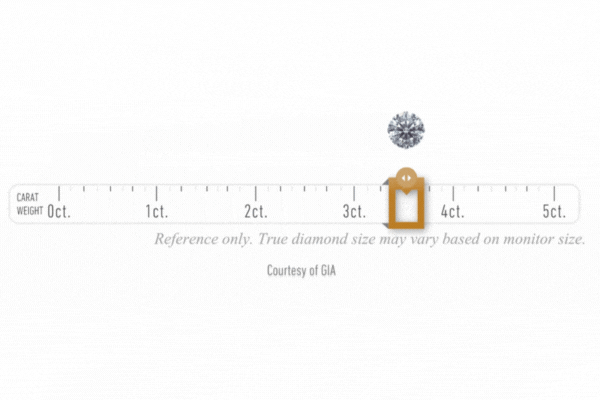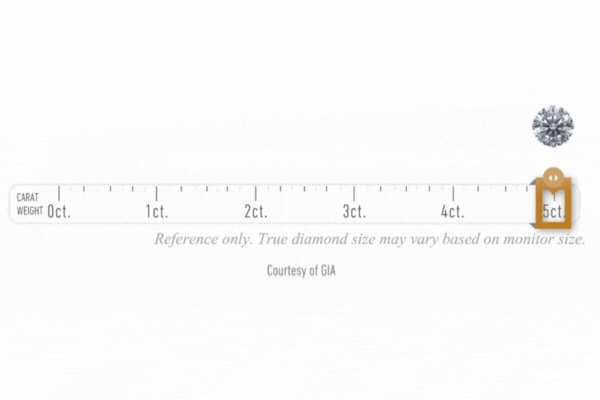
Diamond Cart
After a diamond’s carat weight is determined, its measurements, depth, table, angles, culet, and girdle thickness are recorded.

Diamond Color
A diamond’s color is graded on a scale ranging from d (colorless) to z (light yellow) by comparing it to master stones of predetermined color.
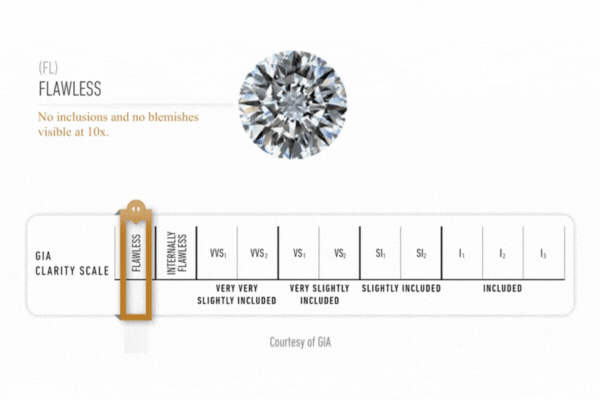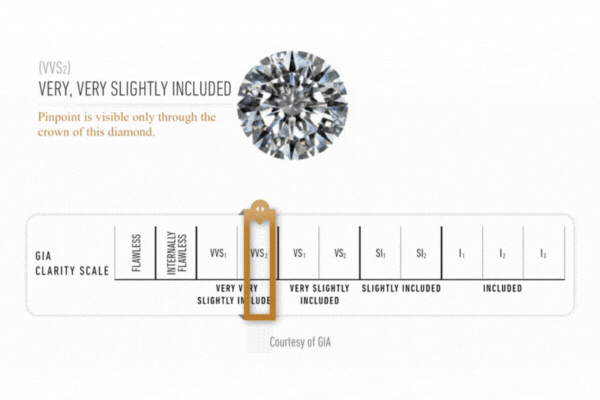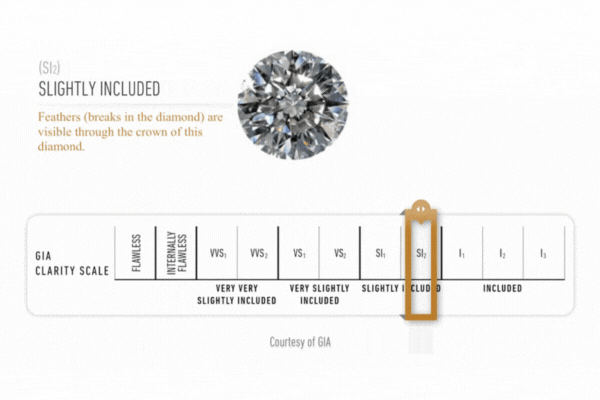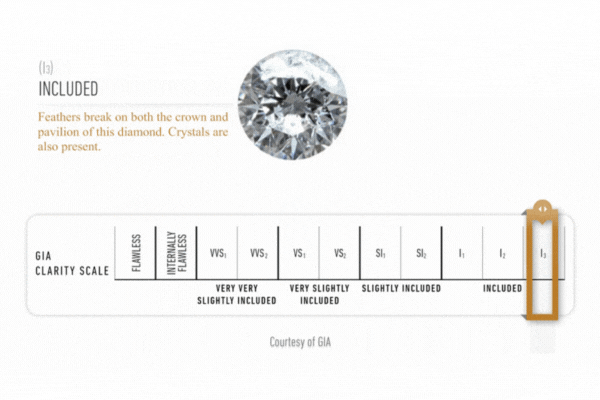
Diamond Clarity
Clarity is assessed on a scale ranging from fl (flawless) to is (included) based on an examination of the stone under a binocular microscope of 10x magnification. the stone’s characteristics are plotted on a diamond diagram.

Diamond Cut Grade
The cut grade is established for brilliant round-cut diamonds based on the analysis of the stone’s craftsmanship and light interaction. the level of a diamond’s craftsmanship is determined by evaluating its polish, symmetry, and proportions. the stone’s light interaction is based on its brightness, scintillation, and fire. the GIA designates the quality of a cut on a grading scale ranging from exr.cellent to poor.
Polish & Symmetry
A diamond is evaluated for polish and symmetry on a grading scale ranging from excellent to poor. the grade is based on an inspection of the diamond’s craftsmanship.
Diamond Fluorescence
A diamond’s fluorescence is determined as none, faint, medium, or strong based on its reaction to ultraviolet light.
Laser Inscription
For added security and identification, a diamond’s girdle can be laser inscribed with its GIA report number. The gia offers laser inscription services for all of the loose diamonds they grade.
GIA Diamond Grading
The GIA Diamond Grading Report is issued for diamonds that fall in the D-Z color range. This detailed report a full quality analysis of shape and cutting style, measurements, carat weight, color grade, clarity grade, cut grade (for brilliant round-cut diamonds), polish and symmetry assessments, and fluorescence. The report also includes a plotted diagram indicating the relative size and location of clarity characteristics, a proportion diagram, and GIA grading scales.
Independent Diamond Certification
What is diamond certification, and how are diamonds independently certified? Independent certification is your assurance that you’re getting a quality diamond that is accurately graded without bias.
Before being purchased, many diamonds are sent to a third-party laboratory for comprehensive evaluation; this process is known in the industry as diamond certification. A respectable laboratory is one staffed by professional gemmologists who specialise in diamond grading. The diamond’s clarity, color, cut and weight is measured using a jeweler’s loupe, microscope, and other industry tools.
Laboratory certification provides an impartial judgement of the quality and characteristics of each diamond. The certificate (called a grading report or dossier) gives the purchaser added confidence that the diamond received is as described by the seller. The certificate is also valuable for insurance purposes, as it provides a professional and independent evaluation of the diamond.
It must be understood that a diamond certificate is not a valuation or appraisal. A valuation or appraisal will establish the value on an item (usually for insurance purposes). A diamond certificate does not assess the diamonds market value, only its characteristics and quality. However, a diamond certificate from a reputable laboratory is very helpful to produce an accurate valuation or appraisal.